Absence Seizures
Absence seizures are short seizures with behavioural arrest and generalised 3-Hertz spike-and-wave discharges on EEG. Absence seizures occur in multiple genetic generalized epilepsies, including Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE), juvenile absence epilepsy (JAE), and Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy (JME).
Pathophysiology
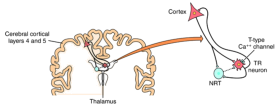 Fig. 1: Thalamocortical circuitry involved in the pathogenesis of absence seizures. Thalamic relay (TR) neurons exhibit spike-wave discharges that result from activation of T-type Ca++ channels, followed by hyperpolarization mediated by GABA released from thalamic reticular (NRT) neurons.
Fig. 1: Thalamocortical circuitry involved in the pathogenesis of absence seizures. Thalamic relay (TR) neurons exhibit spike-wave discharges that result from activation of T-type Ca++ channels, followed by hyperpolarization mediated by GABA released from thalamic reticular (NRT) neurons.
- The pathogenesis of absence seizures involves the cortico-thalamic-cortical circuit[1]
- Glutamatergic neurons from cortical layer VI send activation signals down to the thalamus' nucleus reticularis
- Excitatory thalamic relay neurons connect to cortical pyramidal neurons and produce rhythmic oscillatory neuronal firing between these two regions of the brain
- The thalamic nucleus reticularis' neurons can fire rhythmically (for example, to generate sleep spindles) or constantly in single spikes
- Spikes in thalamocortical networks and thalamic nucleus reticularis neurons influence these firing patterns
- Inhibitory GABA-ergic projections from thalamic nucleus reticularis neurons connect with other neurons and thalamic relay neurons, but not with the cortex.
- An aberrant oscillatory rhythm can result from T-type channel defects or enhanced GABA-B activity. T-type calcium channels act as low-threshold transient calcium channels. After depolarization, T-type channels momentarily allow calcium in before inactivating. Reactivation requires a protracted GABA-B receptor-facilitated hyperpolarization.
Hence T-type calcium channel suppressors like ethosuximide and valproate are used for treating absence seizures. GABA-A agonists like benzodiazepines that preferentially activate thalamic nucleus reticularis neurons can also decrease absence seizures. However Vigabatrin, which increases GABA-B activity will increase absence seizures. Other medications which can worsen absence seizures are sodium channel blockers like Carbamazepine, phenytoin and gabapentin.
[PMID: 22989853] [DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.08.008]

Discussion