Article Index
Page 7 of 19
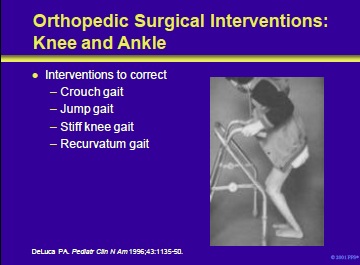
Orthopedic surgical intervention can be used to correct abnormalities of the ankle and knee in patients with cerebral palsy.
Potential problems include:
- Crouch gait is usually iatrogenic.It is recognized by increased hip flexion, increased knee flexion and increased ankle dorsiflexion.
- Jump gait is seen in patients with diplegia or hemiplegia. It is recognized by increased hip flexion, increased knee flexion and increased ankle plantar flexion.
- Stiff knee gait is manifested by swing phase knee stiffness and results in problems with foot clearance. Patients attempt to compensate by hip circumduction, external rotation and contralateral vaulting.
- Recurvatum gait is usually iatrogenic. It is difficult to treat surgically and often requires long leg braces.
The patient shown in the right panel of this slide has a crouch gait. This presentation is common in patients with cerebral palsy and results from hamstring spasticity. It may be exacerbated by prolonged positioning in a seated position. It can be improved by hamstring lengthening.
